Multidentate polyoxometalate modification of metal nanoparticles with tunable electronic states
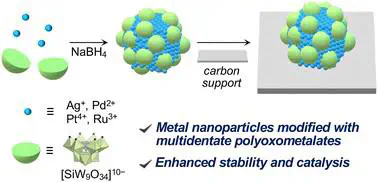 Image credit: RSC
Image credit: RSCAbstract
To respond to the increasing demands for practical applications, stabilization and property modulation of metal nanoparticles have emerged as a key research subject. Herein, we present a viable protocol for preparing small metal nanoparticles (<5 nm; Ag, Pd, Pt, and Ru) via multidentate polyoxometalate (POM, [SiW9O34]10−) modification. In addition to enhancing stability, the POMs can modulate the electronic states of metal nanoparticles. Moreover, immobilization of the POM-modified metal nanoparticles on solid supports enables further tuning of the electronic states via a cooperative effect between the POMs and the supports without altering the particle size. Notably, POM-modified Pd nanoparticles on carbon support exhibited superior catalytic activity and selectivity in hydrogenation reactions in comparison with the catalyst without the POM modification.